Clinical Library
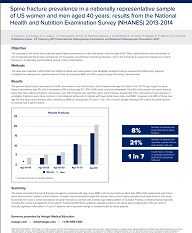
The purpose of this study was to identify spinal fracture prevalence in men and women... Show more
The purpose of this study was to identify spinal fracture prevalence in men and women over the age of 40. Often, spinal fractures are overlooked or not recognized and these types of fractures are frequently of substantial medical significance. This is the first study to assess the prevalence of spine fractures in a nationally representative sample of the United States.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

The goal of this study was to evaluate the precision of bone density measurements made with the... Show more
The goal of this study was to evaluate the precision of bone density measurements made with the Hologic Horizon® and Discovery models and whether the number of vertebrae measured affected the precision.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Introduction: The Horizon® DXA systems are Hologic’s latest generation of bone... Show more
Introduction: The Horizon® DXA systems are Hologic’s latest generation of bone densitometers and the only densitometers to use ultra-fast, high output ceramic detectors and a high frequency, pulsing x-ray generator. Horizon system’s latest digital detector and x-ray technology combine to provide the ability to measure a wide range of clinical patients, including the morbidly obese, with unsurpassed image quality and long-term stability, all in a flexible platform designed for future enhancements.
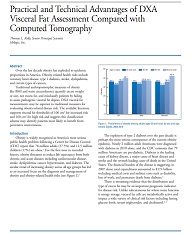
Abstract: Over the last decade obesity has exploded to epidemic proportions in America.... Show more
Abstract: Over the last decade obesity has exploded to epidemic proportions in America. Obesity-related health risks include coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, dyslipidemia,
and certain types of cancers. Traditional anthropomorphic measures of obesity like BMI and waist circumference quantify excess weight or size, not excess fat, and misclassify patients by failing to assess pathogenic visceral fat depots. DXA visceral fat measurements may be superior to traditional measures for evaluating obesity-related disease risk. The available literature supports visceral fat thresholds of 100 cm2 for increased risk and 160 cm2 for high risk and suggests this classification scheme may identify patients most likely to benefit from preventive interventions.

This paper addresses practical considerations for upgrading DXA systems that will help... Show more
This paper addresses practical considerations for upgrading DXA systems that will help clinicians properly migrate data and calibrate equipment, so that patient care is uninterrupted.

Practical considerations for upgrading DXA systems that will help clinicians properly migrate... Show more
Practical considerations for upgrading DXA systems that will help clinicians properly migrate data and calibrate equipment, so that patient care is uninterrupted.

Clinical Summary of Trexler JSCR 2017.
The purpose of this study was to characterize... Show more
Clinical Summary of Trexler JSCR 2017.
The purpose of this study was to characterize Fat-free Mass Index (FFMI) in collegiate American football players and to determine if FFMI varies with different position, division or age groups. According to earlier research FFMI is a height-adjusted assessment of fat-free mass (FFM), which is derived by dividing FFM (in kilograms) by height (in square meters). Further research suggested a natural upper limit of 25 kg·m2 in resistance trained male athletes. At first FFMI was used as a diagnostic value to identify protein-energy malnutrition in those
with low FFM but now it is believed that this value may have valuable applications to a variety of sports. It is believed that FFMI may assist in distinguishing interposition differences comparable to metrics like weight, body mass index, and body fat percentage but may relate more directly to the ability of a player for strength and power.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
The use of dual-energy X-Ray absorptiometry (DXA) has progressively increased in the assessment... Show more
The use of dual-energy X-Ray absorptiometry (DXA) has progressively increased in the assessment of irregularities in body composition commonly correlated with disorders such as obesity, sarcopenia, diabetes, anorexia, human immunodeficiency virus, lipodystrophy, malabsorption and neuromuscular disorders. Athletes also use body composition measurements because increases in lean mass lead to increases in strength, power, agility and overall athletic performance. The purpose of this research was to ascertain the short-term in vivo accuracy and least significant change in serial body composition dynamics provided by the Hologic Horizon A densitometer as currently no published, peer-reviewed body composition accuracy data exists on Horizon scanners in medical literature.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
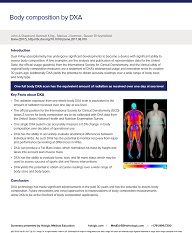
Dual X-Ray absorptiometry has undergone significant developments to become a device with... Show more
Dual X-Ray absorptiometry has undergone significant developments to become a device with significant ability to assess body composition. A few examples are the analysis and publication of representative data for the United State, the official usage guidance from the International Society for Clinical Densitometry, and the clinical utility of regional body composition measures are a testament of DXA’s widespread usage and innovation since its creation 30 years ago. Additionally DXA yields the potential to obtain accurate readings over a wide range of body sizes and body type.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
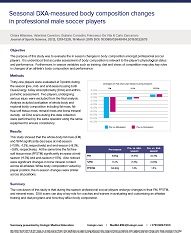
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the in season changes in body composition amongst... Show more
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the in season changes in body composition amongst professional soccer players. It is understood that accurate assessment of body composition is relevant to the player’s physiological status and performance. Furthermore, in season variables such as training, diet and stress of competition may play key roles in changes of an athlete’s body composition and performance.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

This paper presents a technical discussion of advanced body composition reporting and... Show more
This paper presents a technical discussion of advanced body composition reporting and interpretation. Clinical studies have demonstrated that abnormalities in body composition are a key predictor of health risks, including obesity-related diseases, sarcopenia, and lipodystrophy. The ability to reliably and accurately measure body composition, and present the data in a usable format, enables healthcare providers to identify patients at risk for disease and define and manage treatment programs.
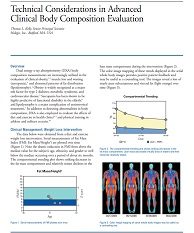
Overview: Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are increasingly... Show more
Overview: Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are increasingly utilized in the evaluation of clinical obesity,1,2 muscle loss and wasting (sarcopenia),3 and abnormal patterns of fat distribution (lipodystrophy).4 Obesity is widely recognized as a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease.5 Sarcopenia has been shown to be highly predictive of functional disability in the elderly,6 and lipodystrophy is a major complication of antiretroviral treatments.7 In addition to detecting abnormalities in body composition, DXA is also employed to evaluate the effects of diet and exercise in health clinics8, 9 and physical training in athletes and military recruits.10
Page 2 of 3
