Clinical Library

Authored by Lars Grimm, MD, MHS, this white paper will cover the benefits of tomosynthesis... Show more
Authored by Lars Grimm, MD, MHS, this white paper will cover the benefits of tomosynthesis guided biopsy in comparison to traditional two-dimensional mammographic guided biopsies. Specifically, this paper will apply to the Hologic Affirm® Prone Biopsy System and the Affirm® Breast Biopsy Guidance System for the Selenia® Dimensions® and 3Dimensions™ mammography Systems.
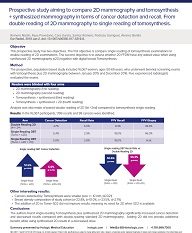
This prospective study has two objectives. The first objective is compare single reading of... Show more
This prospective study has two objectives. The first objective is compare single reading of tomosynthesis examinations to double reading of 2D examinations. The second objective is to assess whether 2D FFDM have any added value when using synthesized 2D mammography (s2D) together with digital breast Tomosynthesis.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

The article first compares the sensitivity and specificity of contrast-enhanced digital... Show more
The article first compares the sensitivity and specificity of contrast-enhanced digital mammography (CEDM) to breast MRI. The next portion lays the foundation for CEDM as a diagnostic alternative to breast MRI based on cost, equipment, and patient access to these modalities.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Authored by Andrew Smith, Ph.D, this white paper will cover the history of breast compression... Show more
Authored by Andrew Smith, Ph.D, this white paper will cover the history of breast compression and approaches Hologic employs to reduce discomfort during mammography imaging. In particular, it will discuss the newest product in the Hologic portfolio, the SmartCurve™ breast stabilization system, designed to greatly improve comfort during breast compression, especially for women who experience pain using conventional flat compression paddles.
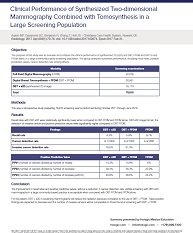
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the clinical performance of synthesized... Show more
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the clinical performance of synthesized 2D (s2D) and DBT, FFDM and DBT to and FFDM alone, in a large community based screening population. The group analyzed outcomes performance, including recall rates, positive predictive values, cancer detection rate among others.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
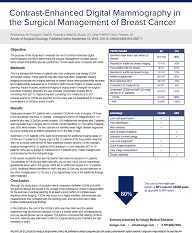
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of contrast-enhanced digital mammography... Show more
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of contrast-enhanced digital mammography (CEDM) in determining the surgical management of breast cancer. When breast MRI (bMRI) was also performed, CEDM results were compared with bMRI.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Clinical Summary of Zuckerman SP et al 2016
The goal of this study was to compare the... Show more
Clinical Summary of Zuckerman SP et al 2016
The goal of this study was to compare the performance of synthesized 2D mammography in a screening population utilizing only digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) with a generated 2D images. A comparison of recall rates and cancer
detection rates to prior outcomes of full field digital mammography (FFDM) and DBT.
Visit PubMed for the full text article.

Clinical Summary of McDonald ES et al 2016
This study of breast cancer screening published... Show more
Clinical Summary of McDonald ES et al 2016
This study of breast cancer screening published online by JAMA Oncology suggests digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) outcomes were sustainable with significant reduction in patient recall, increasing cancer cases per recalled
patients and a decline in interval cancers.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Clinical Summary of Fajardo LL et al 2016
The goal of this pilot study was to compare... Show more
Clinical Summary of Fajardo LL et al 2016
The goal of this pilot study was to compare characterization and conspicuity of common breast lesions imaged by two different scan angles, 15° and 30° angles, in patients with BI-RADS 0 assessment on FFDM examinations. Image quality concerning the elimination of superimposed tissue and overall DBT preference was also evaluated.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Clinical Summary of Rafferty EA et al 2016
Using data from their previous multicenter study,... Show more
Clinical Summary of Rafferty EA et al 2016
Using data from their previous multicenter study, the authors evaluated the differential screening performance of digital mammography combined with tomosynthesis compared with digital mammography alone as a function of breast density.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
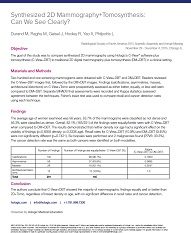
Clinical Summary of Durand M et al 2015, presented at the Radiological Society of North America... Show more
Clinical Summary of Durand M et al 2015, presented at the Radiological Society of North America 2015 Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting.
The goal of this study was to compare synthesized 2D mammography using Hologic’s C-View™ software plus
tomosynthesis (C-View+DBT) to traditional 2D digital mammography plus tomosynthesis (DM+DBT) in a clinical setting.
View the abstract on the RSNA website.

Clinical Summary of Zuckerman S et al 2015
The goal of this study was to evaluate a population... Show more
Clinical Summary of Zuckerman S et al 2015
The goal of this study was to evaluate a population screened entirely with synthesized 2D digital mammograms using Hologic’s C-View™ software plus tomosynthesis (C-View+DBT). Recall rates and recall finding types from the C-View+DBT population were compared to similar historic outcomes from traditional digital mammography plus tomosynthesis screening (DM+DBT).
Page 3 of 4
