Click the title for more information on a clinical resource. To download a PDF file, click the Download button.

A case study by Donald Dengel, PhD, Preofessor, Excercise Physiology, University of Michigan. This... Show more
A case study by Donald Dengel, PhD, Preofessor, Excercise Physiology, University of Michigan. This study reviews how the Horizon® DXA System and body composition analysis creates a symbiotic relationship between collegiate research and athletics

The purpose of this study was to use dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) derived total and regional... Show more
The purpose of this study was to use dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) derived total and regional body composition measures to
define position specific characteristics in a large cohort of National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division 1 football athletes
(n=467)1.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Authored by Y.M. Cheung, G. Roff, M. Grossman
This clinical summary discusses why the need... Show more
Authored by Y.M. Cheung, G. Roff, M. Grossman
This clinical summary discusses why the need to understand the impact of excess fat and fat distribution in individuals at highest cardiometabolic risk has become increasingly more important, especially in the context of targeting intervention and treatment strategies to those
at greatest risk.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

Authored by Tom Kelly, Hologic, Inc., this paper discusses how DXA continues to represent the... Show more
Authored by Tom Kelly, Hologic, Inc., this paper discusses how DXA continues to represent the gold standard
measurement system for body composition in clinical medicine, research, and athletic applications. Continued development and enhancement by Hologic scientists and engineers will keep Hologic DXA body composition applications on the forefront for years to come.

International Olympic Committee (IOC) remains the major goal of protecting athletes.... Show more
International Olympic Committee (IOC) remains the major goal of protecting athletes. The IOC gathered an expert panel to provide these current updates to the 2005 IOC Consensus Statement on the Female Athlete Triad. The triad had previously been described as the combination of disordered eating (DE) and irregular menstrual cycles which potentially lead to decreases in endogenous estrogen and other hormones which may result in low bone mineral density. The current IOC working group presented an extensive, more comprehensive designation reclassified as “Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport” (RED-S). This syndrome denotes impaired physiological ability and goes beyond the triad of Energy Availability (EA), menstrual function and bone health. RED-S is more of a pattern resulting from relative energy deficiency that affects many aspects of bodily function including metabolic rate, menstrual function, bone health, immunity, protein synthesis as well as cardiovascular and psychological wellbeing. Furthermore, it is marked that comparative energy deficiency also afflicts men.

Authored by Jennifer Ketterly, University of North Carolina, in which she shares a case study... Show more
Authored by Jennifer Ketterly, University of North Carolina, in which she shares a case study about an athlete and Visceral Fat Assessment (VAT) made possible by the Horizon DXA™ System. She goes further into how VAT can be associated with cardiac and metabolic disorders. She also highlights how she uses Hologic DXA™ System with her female athlete with nutritional deficits, bone health concerns due to presenting stress fractures, and utilization of DXA for treatment plan and resolution. Read the Hologic white paper for the complete case analysis for the practicing sports dietitian.

Clinical Summary of Trexler JSCR 2017.
The purpose of this study was to characterize... Show more
Clinical Summary of Trexler JSCR 2017.
The purpose of this study was to characterize Fat-free Mass Index (FFMI) in collegiate American football players and to determine if FFMI varies with different position, division or age groups. According to earlier research FFMI is a height-adjusted assessment of fat-free mass (FFM), which is derived by dividing FFM (in kilograms) by height (in square meters). Further research suggested a natural upper limit of 25 kg·m2 in resistance trained male athletes. At first FFMI was used as a diagnostic value to identify protein-energy malnutrition in those
with low FFM but now it is believed that this value may have valuable applications to a variety of sports. It is believed that FFMI may assist in distinguishing interposition differences comparable to metrics like weight, body mass index, and body fat percentage but may relate more directly to the ability of a player for strength and power.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
The use of dual-energy X-Ray absorptiometry (DXA) has progressively increased in the assessment... Show more
The use of dual-energy X-Ray absorptiometry (DXA) has progressively increased in the assessment of irregularities in body composition commonly correlated with disorders such as obesity, sarcopenia, diabetes, anorexia, human immunodeficiency virus, lipodystrophy, malabsorption and neuromuscular disorders. Athletes also use body composition measurements because increases in lean mass lead to increases in strength, power, agility and overall athletic performance. The purpose of this research was to ascertain the short-term in vivo accuracy and least significant change in serial body composition dynamics provided by the Hologic Horizon A densitometer as currently no published, peer-reviewed body composition accuracy data exists on Horizon scanners in medical literature.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
Dual X-Ray absorptiometry has undergone significant developments to become a device with... Show more
Dual X-Ray absorptiometry has undergone significant developments to become a device with significant ability to assess body composition. A few examples are the analysis and publication of representative data for the United State, the official usage guidance from the International Society for Clinical Densitometry, and the clinical utility of regional body composition measures are a testament of DXA’s widespread usage and innovation since its creation 30 years ago. Additionally DXA yields the potential to obtain accurate readings over a wide range of body sizes and body type.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.
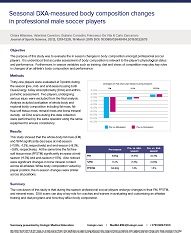
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the in season changes in body composition amongst... Show more
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the in season changes in body composition amongst professional soccer players. It is understood that accurate assessment of body composition is relevant to the player’s physiological status and performance. Furthermore, in season variables such as training, diet and stress of competition may play key roles in changes of an athlete’s body composition and performance.
Please visit PubMed for the full text article.

This paper presents a technical discussion of advanced body composition reporting and... Show more
This paper presents a technical discussion of advanced body composition reporting and interpretation. Clinical studies have demonstrated that abnormalities in body composition are a key predictor of health risks, including obesity-related diseases, sarcopenia, and lipodystrophy. The ability to reliably and accurately measure body composition, and present the data in a usable format, enables healthcare providers to identify patients at risk for disease and define and manage treatment programs.
Overview: Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are increasingly... Show more
Overview: Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are increasingly utilized in the evaluation of clinical obesity,1,2 muscle loss and wasting (sarcopenia),3 and abnormal patterns of fat distribution (lipodystrophy).4 Obesity is widely recognized as a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease.5 Sarcopenia has been shown to be highly predictive of functional disability in the elderly,6 and lipodystrophy is a major complication of antiretroviral treatments.7 In addition to detecting abnormalities in body composition, DXA is also employed to evaluate the effects of diet and exercise in health clinics8, 9 and physical training in athletes and military recruits.10